Introduction
Thermoforming molds are transforming the way manufacturers shape plastic sheets into various products. This process has grown increasingly popular across several industries due to its cost-effectiveness, efficiency, and versatility. Thermoforming, a process in which a plastic sheet is heated to a pliable forming temperature, is then shaped in a mold and cooled into a specific form, has found a prominent place in the production of packaging, automotive parts, and consumer goods.
In this article, we will explore how thermoforming molds are revolutionizing plastic sheet shaping, highlighting the benefits, technology, and applications that make them indispensable in modern manufacturing.
What is Thermoforming?
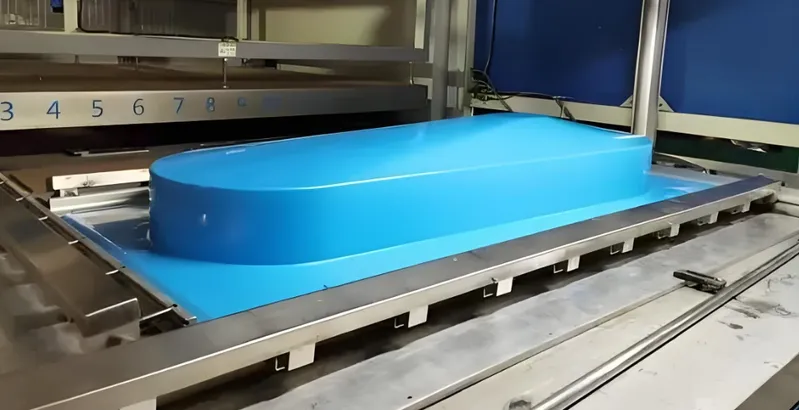
Thermoforming is a manufacturing process that involves heating a plastic sheet until it becomes soft and pliable. Once heated, the sheet is placed into a mold where it is shaped using pressure, vacuum, or mechanical force. After the plastic cools and solidifies, it is removed from the mold and trimmed to create the final product.
There are several types of thermoforming processes, including:
- Vacuum Forming: The plastic sheet is heated and then pulled into a mold by a vacuum, ensuring it conforms to the mold’s shape.
- Pressure Forming: Similar to vacuum forming, but instead of a vacuum, positive air pressure is used to push the sheet into the mold.
- Stretch Forming: The plastic sheet is stretched over a mold to achieve more precise contours, often used for parts with deep draw requirements.
- Plug-Assisted Forming: A combination of pressure and mechanical assistance to ensure precise shaping of deeper and more complex features.
The Revolutionizing Power of Thermoforming Molds
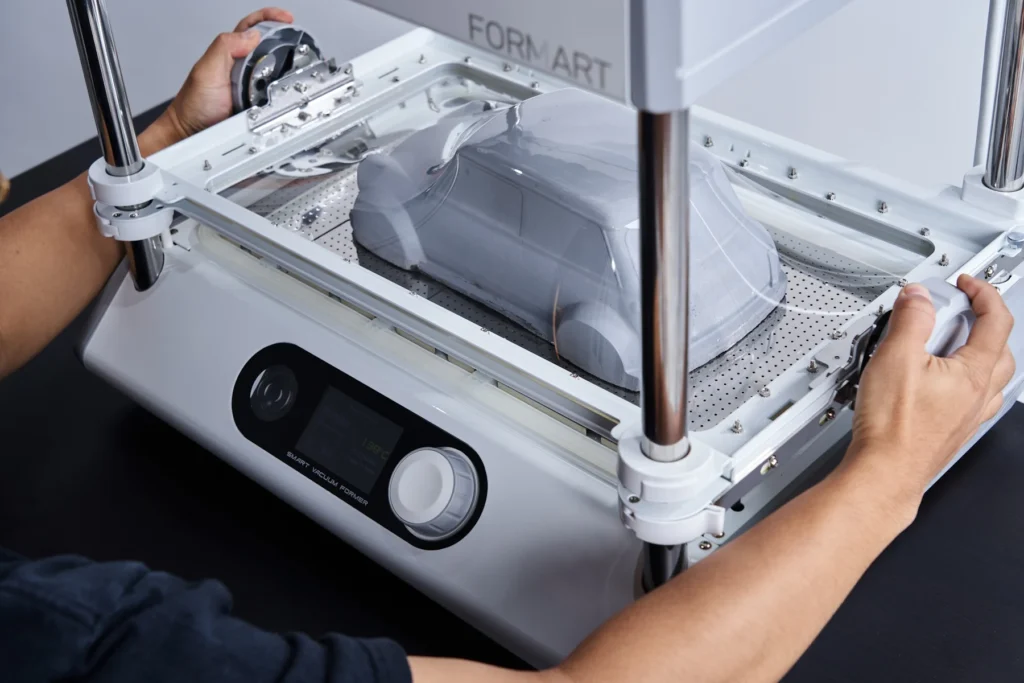

1. Cost-Effective Manufacturing
One of the most significant advantages of thermoforming molds is the cost-effectiveness of the entire process. Unlike injection molding or other techniques, thermoforming molds are relatively inexpensive to produce. The molds can be created using aluminum or steel, and the design complexity can be adjusted to suit different needs, whether for short or large production runs.
- Statistic: Thermoforming molds are approximately 30-50% less expensive to produce compared to injection molds, making them a cost-effective choice for manufacturers with lower-volume production needs.
Thermoforming also requires fewer steps in the production process, reducing both material and labor costs. This allows companies to deliver high-quality products at competitive prices, particularly in industries that rely on packaging, consumer goods, and automotive parts.
2. Speed and Efficiency in Production
The speed of the thermoforming process makes it ideal for industries that need quick turnaround times. The ability to form plastic sheets rapidly, and the low energy consumption required, gives manufacturers a competitive edge when time-to-market is critical.
- Fact: The typical thermoforming cycle time ranges from 30 seconds to several minutes, depending on the part’s size and complexity. This is significantly faster compared to other molding processes like injection molding.
Additionally, the automation of thermoforming molds allows for increased efficiency in production. Companies can ramp up production quickly, reducing downtime and increasing throughput, which directly contributes to lower production costs and higher output.
3. Material Versatility
Thermoforming molds can work with a wide range of thermoplastic materials, making them incredibly versatile. These materials include high-density polyethylene (HDPE), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), polystyrene (PS), and others. Manufacturers can select the best material for a specific application based on desired properties such as durability, flexibility, and chemical resistance.
- Example: In the packaging industry, thermoforming molds are often used to create containers from clear PVC or PET plastic, allowing consumers to easily view the product inside while ensuring the packaging is sturdy.
This versatility enables manufacturers to create a wide array of products, from simple trays and containers to intricate automotive parts, medical device packaging, and consumer electronics enclosures.
4. Design Flexibility
Thermoforming molds are capable of producing complex shapes and intricate details. The process allows for the creation of deep drawn parts and detailed textures that are not possible with traditional molding methods. The design flexibility of thermoforming makes it a popular choice for industries that require custom-shaped parts or packaging that need to fit specific product dimensions.
- Fact: Thermoforming molds allow for the production of parts with wall thicknesses as thin as 0.020 inches and as thick as 0.125 inches, giving manufacturers the flexibility to meet their design requirements.
In addition, thermoforming molds can be adjusted or modified to accommodate design changes without the need for entirely new molds, offering cost-effective solutions for prototypes and iterative design improvements.
5. Environmental Impact
With growing emphasis on sustainability, thermoforming molds offer an environmentally friendly alternative to traditional molding methods. Since the process requires less energy and generates fewer emissions than some other molding techniques, it is more eco-friendly. Additionally, the materials used in thermoforming can often be recycled or reused, further contributing to reduced environmental impact.
- Statistic: Research suggests that approximately 70% of plastic waste from thermoforming processes can be recycled, which helps reduce waste and conserve resources.
For manufacturers seeking to align with sustainability goals, thermoforming offers an attractive, environmentally-conscious choice that reduces material waste and carbon emissions.
Applications of Thermoforming Molds
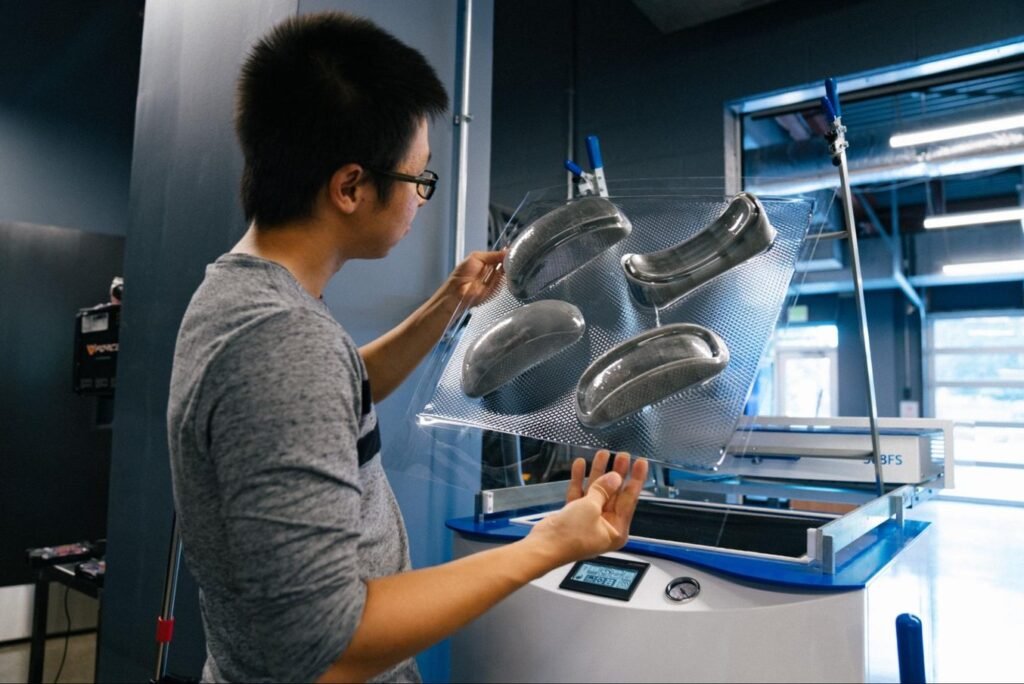

Thermoforming molds are used in a wide range of industries due to their efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and design flexibility. Here are some of the most common applications:
1. Packaging Industry
One of the most prevalent uses of thermoforming molds is in the packaging sector. Thermoforming is used to produce food containers, clamshell packaging, trays, and other protective packaging solutions. The ability to create lightweight yet sturdy packaging helps manufacturers reduce material costs and improve product protection during shipping.
- Example: Vacuum-formed food packaging, such as the plastic trays used for fresh produce or meat, is produced using thermoforming molds. These packages help extend the shelf life of food while offering convenience to consumers.
2. Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, thermoforming is employed to create lightweight and durable parts. Components such as interior panels, trim, and door linings are often produced using thermoforming molds. The speed of production and the ability to achieve lightweight parts with high structural integrity make thermoforming molds an excellent choice for automotive manufacturers.
- Fact: Thermoformed parts in the automotive sector can reduce overall vehicle weight by up to 20%, contributing to fuel efficiency and improved performance.
3. Medical Industry
Thermoforming molds are widely used in the medical industry to produce packaging for medical devices, equipment, and instruments. The precise molding and durability offered by thermoforming molds help protect sensitive medical products during shipping and storage, ensuring that they reach healthcare providers in optimal condition.
- Example: Custom medical packaging made from thermoformed plastics can be used to securely house surgical instruments, keeping them sterile and ready for use.
4. Consumer Goods
Thermoforming is also popular in the production of consumer goods, including trays, appliances, and protective cases. Its ability to produce detailed, functional parts at a low cost makes it ideal for consumer products that require both performance and aesthetic appeal.
- Example: Manufacturers use thermoforming molds to create plastic cases for electronics such as smartphones, ensuring a perfect fit while maintaining a sleek, attractive appearance.
Challenges in Thermoforming and How to Overcome Them
While thermoforming molds offer numerous advantages, there are some challenges that manufacturers may face when using them. Below are some of the key challenges and potential solutions:
1. Material Limitations
Although thermoforming can handle a wide variety of thermoplastic materials, it may not be suitable for materials that require high-temperature processing or those that are particularly brittle.
- Solution: Manufacturers can experiment with different material combinations or consider alternative forming processes if the material requires higher durability or resistance.
2. Part Warping
One of the common challenges with thermoforming is part warping, especially in complex geometries. This occurs when the plastic cools unevenly, causing it to distort.
- Solution: Proper mold design, temperature control, and the use of uniform heating methods can help reduce the risk of warping.
3. Limited Precision for Small Parts
While thermoforming is great for creating large, intricate shapes, it may not always be the best method for producing highly detailed, small parts with extremely tight tolerances.
- Solution: For small parts that require very high precision, manufacturers may need to consider alternative molding techniques, such as injection molding, alongside thermoforming.
Conclusion
Thermoforming molds are revolutionizing the plastic sheet shaping process by offering cost-effective, efficient, and versatile solutions for a wide range of industries. Their ability to produce complex designs, coupled with fast production times and environmentally friendly characteristics, makes them an essential tool in modern manufacturing. As industries continue to evolve, the applications and benefits of thermoforming molds are sure to expand, driving further innovations in product design, manufacturing efficiency, and sustainability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What materials can be used with thermoforming molds?
Thermoforming molds can be used with a wide range of thermoplastics, including PVC, PET, HDPE, PS, and ABS. The material choice depends on the application’s requirements for strength, flexibility, and chemical resistance.
2. How does thermoforming compare to injection molding?
While injection molding is ideal for high-precision parts, thermoforming is often preferred for producing large, lightweight, and low-cost items like packaging and automotive components. Thermoforming molds are also more cost-effective for low to medium production volumes.
3. Can thermoforming be used for small production runs?
Yes, thermoforming is suitable for small production runs, but it becomes particularly cost
Sources:
- “Thermoforming Process: Benefits and Applications,” Plastics Technology, https://www.ptonline.com
- “Understanding Thermoforming,” Thermoforming Institute, https://www.thermoforminginstitute.com
- “Thermoforming and its Applications in Manufacturing,” Plastics News, https://www.plasticsnews.com
- “The Advantages of Thermoforming in Production,” Manufacturing Today, https://www.manufacturingtoday.com