Introduction
In the highly competitive world of mold production, managing supply chain issues is crucial for ensuring consistent product delivery, minimizing costs, and meeting customer demands. As the global supply chain faces ongoing challenges, including material shortages, transportation delays, and fluctuating prices, mold manufacturers are under increasing pressure to find solutions that allow them to remain agile and efficient.
In this article, we’ll explore the key supply chain issues facing mold manufacturers today, the strategies they are implementing to overcome these challenges, and how they can ensure smooth operations despite disruptions.
1. Material Shortages and Price Fluctuations
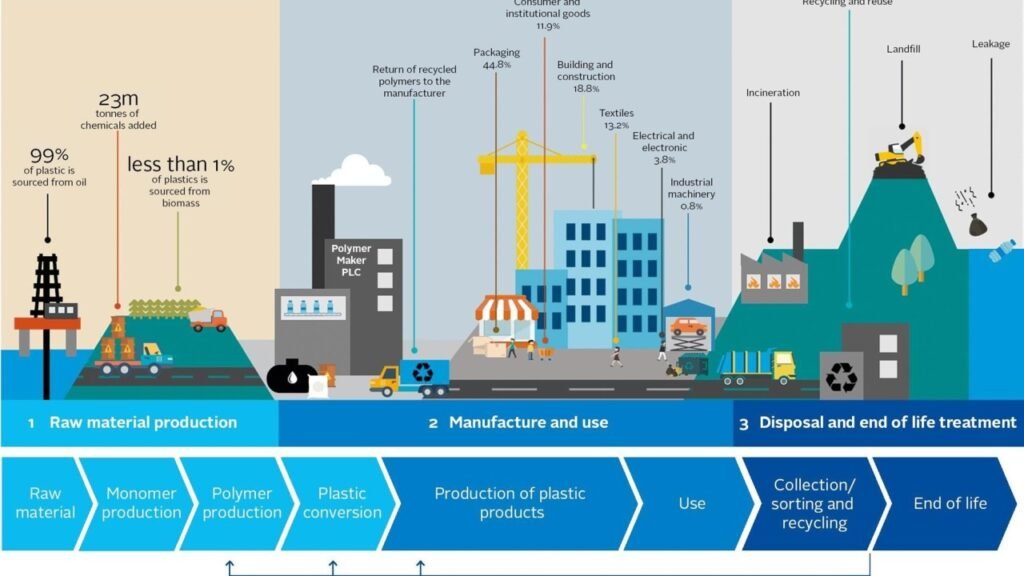
One of the most significant challenges faced by supply chain issues is the shortage of essential materials, such as high-quality steel, aluminum, and specialized alloys. These shortages can lead to delays in mold production and increase the cost of raw materials, putting pressure on margins.
Strategies for Managing Material Shortages:
- Diversifying Suppliers: To mitigate the risk of material shortages, many manufacturers are diversifying their supplier base. By sourcing materials from multiple suppliers, both locally and internationally, they reduce the impact of supply chain issues and a single supply chain disruption. Additionally, regional sourcing helps mitigate the risks associated with global supply chain instability, such as transportation delays or geopolitical tensions.
- Long-Term Supplier Relationships: Building strong, long-term relationships with key suppliers is another strategy that mold manufacturers use. These relationships can lead to more reliable supply chains, priority access to materials during shortages, and better terms on pricing. Manufacturers often collaborate closely with their suppliers to forecast demand and avoid material shortages by ordering materials in advance to help in supply chain issues
- Material Substitution: When faced with a shortage of specific materials, manufacturers may consider material substitution. For example, using alternative alloys or different grades of steel that meet the performance requirements of the mold while ensuring cost-effectiveness and availability. to face supply chain issues
2. Logistics and Transportation Delays
Logistics and transportation issues are a common supply chain issues for mold manufacturers. Delays in shipping, disruptions in the transportation network, and higher fuel costs can result in longer lead times, increased transportation expenses, and missed delivery deadlines.
How Manufacturers Are Addressing Logistics Challenges:
- Collaborative Logistics Management: To reduce transportation delays, mold manufacturers are increasingly adopting collaborative logistics management. By partnering with logistics providers and other manufacturers, they can share transportation routes, reduce costs, and improve the overall efficiency of the supply chain. This can be particularly effective in industries that rely on just-in-time (JIT) inventory systems. to help with supply chain issues
- Technology for Supply Chain Visibility: Manufacturers are leveraging advanced supply chain management software and real-time tracking systems to improve visibility into the status of shipments. This technology allows manufacturers to track the location of raw materials, identify potential delays, and make adjustments in real-time to avoid disruptions. to face supply chain issues
- Stockpiling Critical Materials: In some cases, manufacturers may stockpile critical raw materials or components to protect against transportation delays. This is particularly useful for materials that have long lead times or are in high demand. However, this strategy must be carefully managed to avoid inventory overflow or storage issues and supply chain issues
3. Demand Forecasting and Inventory Management

Accurate demand forecasting and inventory management are essential for ensuring that mold manufacturers have the right materials and components in stock without over-accumulating inventory. Inaccurate demand forecasting can lead to either stockouts or excess inventory, both of which incur costs. and help with supply chain issues
Best Practices for Improving Forecasting and Inventory Management:
- Advanced Forecasting Software: Many mold manufacturers are adopting advanced forecasting software powered by artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning to predict demand with greater accuracy. These tools analyze historical data, customer trends, and market conditions to help manufacturers make informed decisions about purchasing and production schedules. to reduce supply chain issues
- Real-Time Inventory Tracking: Real-time inventory management systems enable mold manufacturers to keep track of raw material quantities and product inventory levels. By integrating these systems with production schedules and supplier delivery times, manufacturers can ensure they have sufficient materials on hand without holding unnecessary inventory that ties up capital. to help with supply chain issues
- Just-in-Time (JIT) Inventory: Some manufacturers rely on JIT inventory systems to minimize storage costs and reduce the risk of overproduction. By aligning inventory levels closely with customer orders and production needs, JIT systems allow manufacturers to respond more dynamically to fluctuations in demand.
4. Managing Global Supply Chain Risks
Global supply chains are increasingly vulnerable to disruptions caused by factors such as natural disasters, political instability, and global pandemics. These disruptions can lead to shortages of materials, delayed shipments, and increased operational costs. and face supply chain issues
Strategies for Managing Global Supply Chain Risks:
- Supply Chain Risk Assessment: Mold manufacturers are conducting regular supply chain issues to identify vulnerabilities in their operations. By mapping their supply chains, evaluating potential risks, and developing contingency plans, they can mitigate the impact of unforeseen disruptions.
- Nearshoring and Local Sourcing: To reduce dependence on international suppliers and mitigate the risks associated with global supply chains, some manufacturers are shifting to nearshoring or local sourcing. By moving production closer to the target market, manufacturers can reduce transportation costs, minimize lead times, and increase flexibility.
- Building Resilience through Diversification: Manufacturers are building resilience by diversifying their supply chain. This involves working with multiple suppliers in different geographic locations to ensure that they have backup sources for critical materials. Diversifying the supply chain also helps prevent disruptions caused by regional factors, such as political instability or extreme weather events.
5. Quality Control and Inspection Challenges
Quality control is crucial in mold manufacturing, as even a small defect in the mold can lead to significant issues in the final product, such as dimensional inaccuracies, poor surface finish, and reduced durability. Ensuring consistent quality control throughout the supply chain can be difficult, especially when working with multiple suppliers and vendors.
Approaches for Enhancing Quality Control:
- Supplier Audits and Certifications: Mold manufacturers are conducting regular supplier audits to ensure that their suppliers adhere to quality standards and regulations. Manufacturers may also require their suppliers to obtain certifications such as ISO 9001, which ensures consistent quality management practices.
- In-House Quality Inspection: Some mold manufacturers are investing in advanced inspection technologies such as coordinate measuring machines (CMM), laser scanning, and X-ray inspection to assess the quality of incoming materials and final molds. These technologies allow for high-precision measurements and ensure that parts meet the required specifications before they are used in production.
- Collaborative Quality Control: By working closely with suppliers and vendors, manufacturers can ensure that quality control processes are standardized and aligned. This collaboration helps identify potential quality issues early in the production process, reducing the risk of defects.
6. Overcoming Talent Shortages and Skills Gaps
In addition to material and logistics challenges, many mold manufacturers also face difficulty finding and retaining skilled workers. The demand for high-quality craftsmanship, advanced technical skills, and engineering expertise in mold design and production is growing, but the available talent pool is limited.
Solutions to Address Talent Shortages:
- Training and Upskilling Programs: To address the skills gap, many manufacturers are offering training and upskilling programs to ensure that their employees have the technical knowledge necessary to operate advanced machinery and implement modern manufacturing techniques. These programs may also focus on lean manufacturing, quality control, and maintenance practices.
- Collaboration with Educational Institutions: Some mold manufacturers are partnering with colleges and technical schools to develop tailored programs that produce skilled workers specifically trained in mold-making processes. By working closely with academic institutions, manufacturers can ensure a steady supply of talent with the right skills for the industry.
- Automation and Robotics: The adoption of robotic automation and artificial intelligence helps mitigate the impact of labor shortages. Automated systems can perform repetitive tasks, improve consistency, and free up skilled workers to focus on higher-value activities.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: How can mold manufacturers manage material shortages?
A: By diversifying suppliers, building long-term relationships with key partners, and exploring material substitution options, manufacturers can minimize the impact of material shortages.
Q2: What role does technology play in overcoming supply chain issues?
A: Technology such as real-time tracking, advanced forecasting, and supply chain management software provides greater visibility, better decision-making, and faster responses to disruptions.
Q3: How can manufacturers ensure the quality of materials from suppliers?
A: Regular audits, quality certifications, and in-house inspection technologies like CMM and laser scanning ensure that materials meet required specifications before being used in production.
Q4: How do mold manufacturers mitigate global supply chain risks?
A: Manufacturers can mitigate risks by conducting supply chain risk assessments, nearshoring, local sourcing, and diversifying suppliers to ensure resilience in case of disruptions.
Q5: What is the impact of labor shortages on mold manufacturing?
A: Labor shortages can affect production schedules and quality control. Manufacturers address this by offering training programs, collaborating with educational institutions, and adopting automation technologies.
Sources:
- MoldMaking Technology – “Navigating Supply Chain Challenges in Mold Manufacturing”
- Plastics Technology – “Material Shortages: How Mold Manufacturers Are Adapting”
- Supply Chain Management Review – “Innovations in Logistics and Transportation for Manufacturers”