Introduction
In the ever-evolving world of manufacturing, precision and efficiency are non-negotiable. One of the most transformative technologies in recent years is CNC machining in mold making. From reducing production time to ensuring unmatched precision, CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines are not just an improvement—they’re a game changer. This article dives deep into the rise of CNC machining in the mold industry, detailing how it works, why it’s essential, and the immense value it offers manufacturers worldwide.
The Evolution of Mold Making
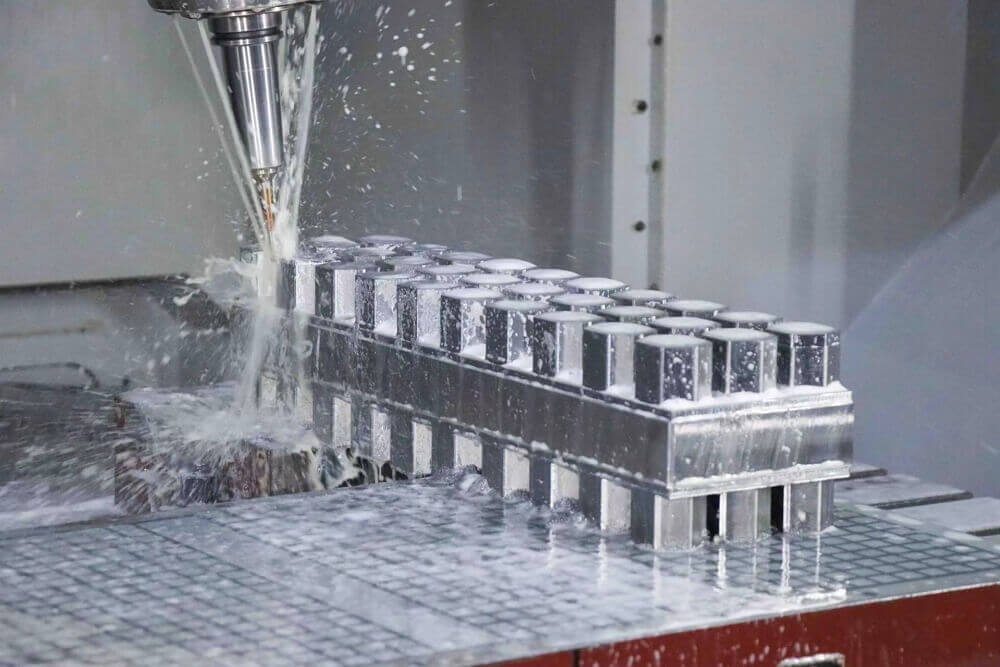

Mold making has come a long way from the manual and semi-automated processes of the past. Previously, mold manufacturing relied heavily on skilled labor, manual lathes, and grinders, which were time-consuming and often prone to human error. In contrast, CNC machining leverages computerized controls to remove material from a workpiece with high-speed rotating tools, resulting in precise, repeatable molds every time.
How CNC Machining Works in Mold Making
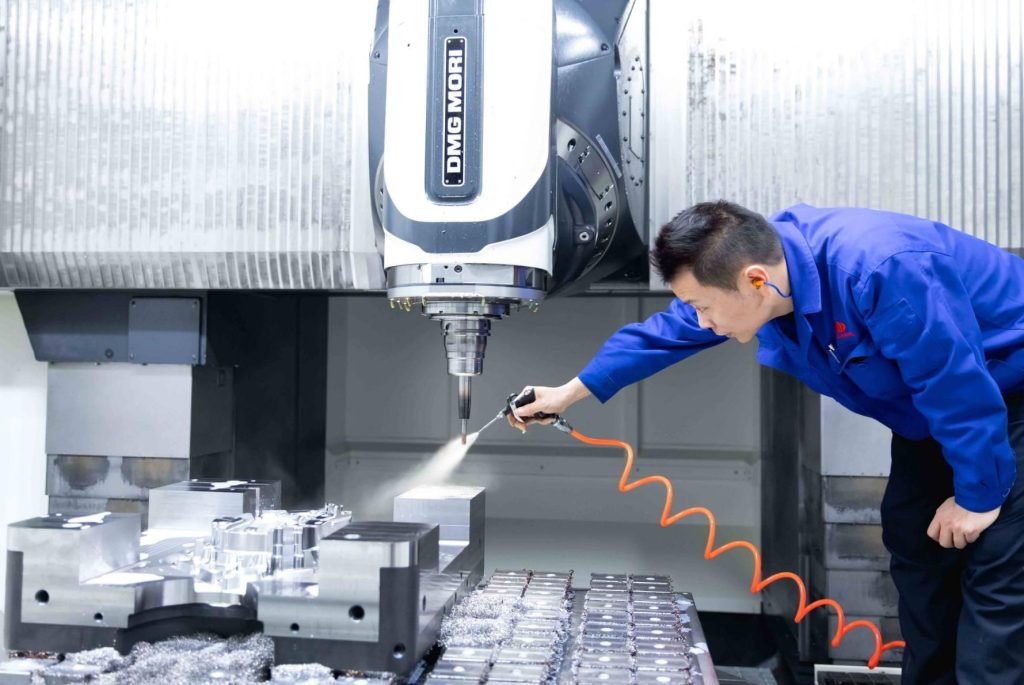

CNC machining starts with a digital CAD (Computer-Aided Design) file, which defines the mold’s geometry. This file is then translated into a CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) program that controls the machine’s cutting tools.
Main steps:
- Design: A 3D model of the mold is created.
- Toolpath Generation: CAM software calculates the optimal tool paths.
- Setup: Raw materials are secured on the CNC machine.
- Machining: The CNC machine performs the cutting operations with micrometer-level precision.
- Finishing: Surfaces are polished, and final quality checks are done.
Benefits of CNC Machining in Mold Making
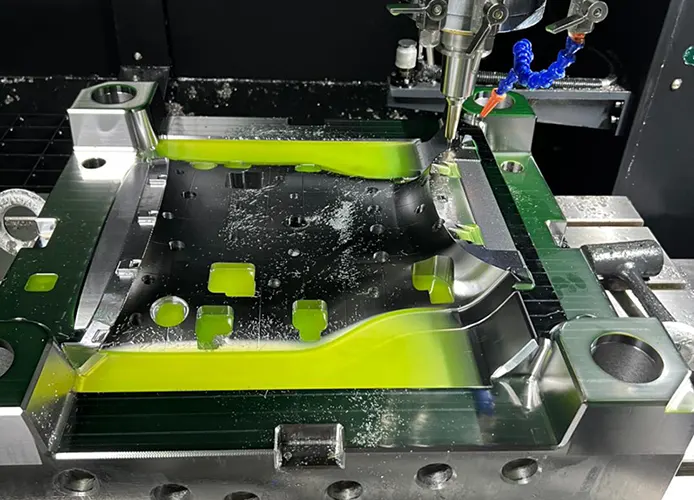
1. Unmatched Precision
CNC machining can achieve tolerances as tight as ±0.005 mm. This level of accuracy is essential for applications like medical devices, aerospace parts, and micro-injection molding.
2. Reduced Production Time
Automated tool changes, high-speed cutting, and minimized rework reduce production time significantly. For example, what once took 2–3 weeks in traditional mold making can now be achieved in just 5–7 days.
3. Repeatability and Consistency
Once a CAD file is created, CNC machines can reproduce the exact same mold hundreds or even thousands of times, ensuring consistency across production batches.
4. Material Versatility
CNC machines can work with a wide range of materials including:
- Tool steels (H13, P20)
- Aluminum
- Copper alloys
- Plastics
5. Cost Efficiency
Though CNC machines require high initial investment, they reduce labor costs and waste. The ROI becomes evident with high-volume or complex mold production.
Real-World Applications and Statistics
- Automotive Industry: CNC molds are used for dashboards, bumpers, and engine components. The automotive tooling market was valued at over $18 billion in 2023, with CNC machining playing a major role.
- Medical Devices: Custom medical parts require micro-precision. CNC’s accuracy reduces post-processing by up to 30%.
- Electronics: For mobile devices, CNC allows high-density and miniature component molds with tight tolerances.
- Aerospace: Aerospace parts demand flawless consistency. CNC machining reduces defect rates by over 40% compared to manual techniques.
Challenges in CNC Mold Making
Despite its advantages, CNC machining has its own set of challenges:
- High Initial Costs: CNC machines range from $50,000 to $500,000.
- Skilled Operators: Operating and programming CNC machines requires trained personnel.
- Tool Wear and Maintenance: Constant maintenance is needed to ensure consistent output.
Future Trends in CNC Mold Making
- AI and Machine Learning: Predictive maintenance and automatic optimization are already being integrated into advanced CNC systems.
- 5-Axis Machining: Enables more complex geometries and fewer setups.
- Hybrid Manufacturing: Combining CNC with additive manufacturing is on the rise.
- Remote Monitoring: Cloud-connected CNC machines allow real-time status tracking and diagnostics.
Conclusion
CNC machining in mold making is more than just a technological upgrade—it’s a revolution that’s redefining what’s possible in manufacturing. Its blend of precision, speed, and adaptability makes it indispensable for industries that demand quality and scalability. As industries grow more competitive, CNC will continue to be the cornerstone of efficient and cost-effective mold production.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What materials are best suited for CNC mold making?
A: Tool steels like H13 and P20, aluminum, and copper alloys are commonly used due to their machinability and durability.
Q2: How accurate is CNC machining for molds?
A: CNC machining can achieve tolerances as tight as ±0.005 mm, making it suitable for high-precision industries.
Q3: Is CNC machining cost-effective for small production runs?
A: It depends. The setup cost is high, but if precision is essential, CNC is worthwhile even for small batches.
Q4: How long does it take to produce a mold using CNC?
A: Depending on complexity, it can take anywhere from 3 to 10 days, much faster than traditional methods.
Q5: Can CNC machining be used for plastic molds?
A: Yes, CNC machining is ideal for producing both metal molds used in plastic injection and direct machining of plastic mold components.
Sources:
- MoldMaking Technology Magazine
- International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology
- Statista: Tooling Market Data
- Modern Machine Shop – CNC in Tooling
- SME Manufacturing Reports