Introduction
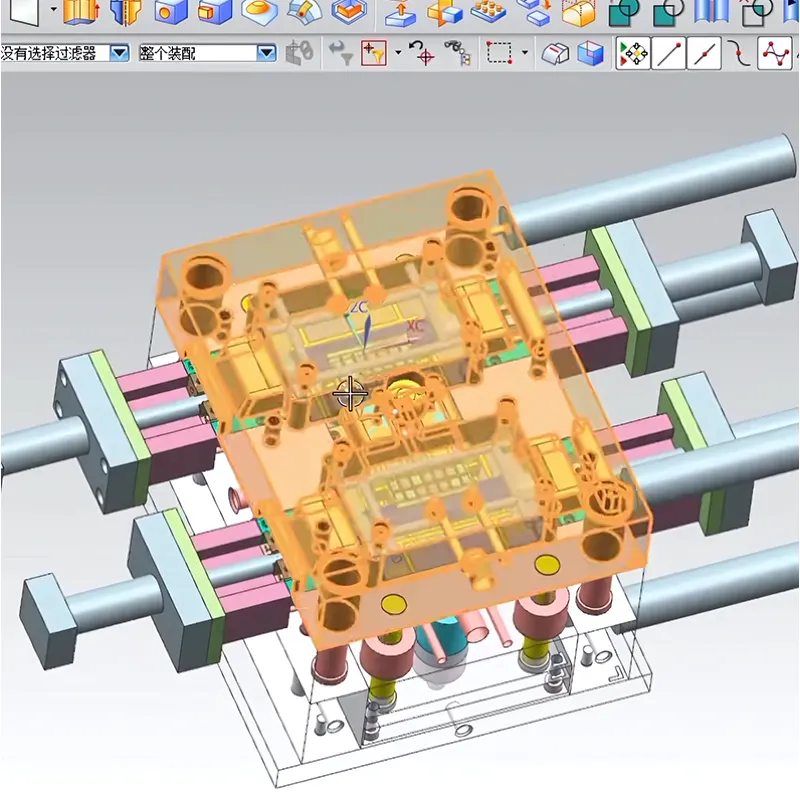
In today’s highly competitive manufacturing landscape, the quality in custom mold design is more than a technical requirement — it’s a business imperative. Custom molds are essential for industries like automotive, medical devices, packaging, electronics, and consumer goods, where product consistency, durability, and dimensional accuracy are non-negotiable.
A single defect in a mold can lead to thousands of flawed products, production delays, and wasted resources. That’s why ensuring the highest standards in mold design isn’t just about aesthetics — it directly impacts performance, safety, compliance, and profitability.
This article explores how manufacturers and mold designers can guarantee exceptional quality in custom mold design projects, supported by real-world examples, best practices, tools, and industry statistics.
Why Quality Matters in Custom Mold Design
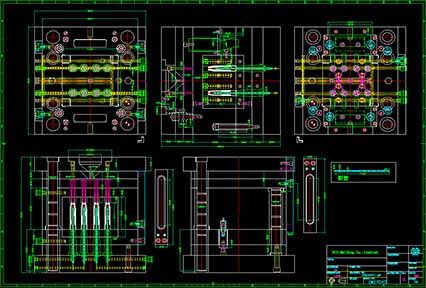
Quality in custom mold design ensures that:
- Molded parts meet dimensional tolerances
- The mold operates efficiently with minimal wear and tear
- Defects like flashing, warping, or short shots are avoided
- Production downtime due to mold failure is minimized
- Client satisfaction and product marketability are maintained
🔍 Statistic: According to a 2023 survey by Plastics News, 64% of mold-related product rejections stem from design flaws or misaligned tolerances — issues that could be prevented with a robust quality in custom mold design assurance process.
Key Components of Quality in Custom Mold Design

1. Detailed Client Requirements and Communication
The foundation of any custom mold project is clear, complete, and consistent communication between the client and the mold maker.
- Gather precise specifications: tolerances, materials, finishes, part geometry, lifecycle.
- Understand application context: Will it be used in high heat? Is it a food-safe product?
- Conduct design for manufacturability (DFM) meetings to assess feasibility and optimize design.
Tip: Use CAD collaboration tools to align expectations early on. Miscommunication at the start is one of the biggest threats to quality in custom mold design
2. Advanced CAD/CAM Software for Mold Design
Using modern design software improves precision, reduces error, and accelerates iteration.
Popular tools include:
- SolidWorks
- Autodesk Moldflow
- Siemens NX
- PTC Creo
These tools support:
- 3D modeling and simulations
- Automated draft analysis
- Wall thickness checking
- Cooling system design
🎯 Example: Siemens NX allows simulation of plastic flow to detect areas of air entrapment or pressure imbalance before physical mold production.
3. Material Selection and Compatibility
Choosing the right material for the mold is as important as the design itself. Common mold materials include:
| Material | Use Case | Properties |
| P20 Steel | General-purpose molds | Moderate hardness, good machinability |
| H13 Steel | High-volume molds | High thermal resistance |
| Aluminum | Prototyping and low-volume | Lightweight, fast machining |
| Beryllium Copper | Complex cooling channels | High thermal conductivity |
Poor material selection can lead to:
- Cracking under thermal stress
- Premature wear
- Corrosion issues (especially in humid environments)
4. Design for Manufacturability (DFM)
A core principle of quality in custom mold design, DFM ensures the mold is optimized for ease of production and long-term reliability.
DFM considerations include:
- Parting lines
- Ejection system design
- Undercuts and draft angles
- Cooling system layout
- Shrinkage compensation
📊 Statistic: Companies that implement DFM in the early stages report up to 30% reduction in mold revision cycles (Source: MoldMaking Technology, 2023).
5. Simulation and Mold Flow Analysis
Before cutting any metal, mold flow simulations help detect and resolve issues like:
- Weld lines
- Sink marks
- Air traps
- Uneven fill patterns
Tools: Autodesk Moldflow, Moldex3D, Simcon Cadmould
Simulations can:
- Reduce mold rework by 50%
- Improve first-time quality
- Save tens of thousands in production costs
6. CNC Precision Machining and Tolerances
Modern CNC machines can achieve tolerances as tight as ±0.001 mm. The precision of machining is vital for:
- Interchangeable inserts
- Fit of complex cavities and cores
- Surface finish and seal integrity
Routine maintenance of CNC machines and skilled operators are key to achieving consistent output.
7. In-Process Quality Checks and Measurements
Throughout the mold making process, several quality assurance checks should be performed:
- First article inspection (FAI)
- Coordinate measuring machine (CMM) checks
- Profile projectors
- Surface roughness testers
- Hardness testers
These help ensure:
- Accuracy of cavities and cores
- Symmetry and alignment
- Material hardness matches specs
8. Prototype Testing and Validation
Creating a prototype mold is one of the best ways to validate your quality in custom mold design before full-scale production. It allows for:
- Real-world testing of molded part
- Evaluation of cooling time, cycle time, and flow
- Client feedback and adjustment
💡 Note: Prototyping may add initial cost but prevents costly rework and delays down the line.
9. Documentation and Traceability
Quality standards like ISO 9001 or IATF 16949 require full traceability of materials, design versions, and quality checks.
Mold makers should document:
- Material certifications
- CAD version history
- Inspection reports
- Heat treatment and coating data
This ensures accountability and allows rapid problem-solving in case of issues during production.
10. Client Sign-Off and Mold Trials
Before delivery, the mold should undergo:
- Trial runs under real production conditions
- Client sign-off with PPAP or FAI documentation
- Sample part evaluation for tolerances and finish
This final stage ensures the mold not only works — but works exactly as required.
Challenges to Watch Out For
| Challenge | Impact |
| Inadequate cooling design | Cycle time increases, poor part finish |
| Tolerance stacking | Assembly issues and defects |
| Improper gate placement | Flow defects, warping |
| Poor venting | Short shots, burn marks |
| Incorrect shrinkage allowance | Dimensional errors |
Avoiding these issues early through quality control saves time, money, and reputation.
Conclusion
Achieving quality in custom mold design is a blend of engineering expertise, cutting-edge tools, and relentless attention to detail. From the initial consultation to the final trial, each step plays a crucial role in ensuring that the mold delivers top performance and meets customer expectations.
By embracing simulation tools, implementing DFM principles, investing in skilled labor, and prioritizing clear documentation, manufacturers can dramatically improve quality in custom mold design outcomes — and win the trust of clients across industries.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What’s the most important factor in ensuring quality in custom mold design?
A: A combination of clear client communication, mold flow analysis, and DFM principles are essential for high-quality results.
Q2: How can I reduce the number of mold revisions?
A: Use simulation tools like Autodesk Moldflow and get client feedback at the prototyping stage.
Q3: Are aluminum molds lower in quality than steel molds?
A: Not necessarily. Aluminum molds are great for low-volume production and prototyping but aren’t suited for high-volume production due to wear.
Q4: What is the typical lifespan of a high-quality mold?
A: With proper material and maintenance, a high-quality steel mold can last for 500,000 to over 1 million cycles.
Q5: How do I choose the right mold material for quality in custom mold design?
A: Consider the production volume, type of plastic used, operating temperatures, and budget.
Sources
- Custom Mold and Design: High-Quality Tooling for Industry
- Essential Mold Design Guide For Designers
- Plastic Injection Mold Manufacturing – Quality Mold, Inc.
- Custom Mold Design & Automation | TN Plastics
- Mold Design & Tooling | Plastic Injection Molding
Suggested Topics
- Plastic Fitting Molds: Ensuring Perfect Fits for Plumbing Systems
- The Ultimate Mold Manufacturing Guide: Techniques, Tips, and Best Practices
- Molds in Packaging: Transforming Efficiency and Sustainability
- Mold Technology Adapting to Market Changes | Innovations in Mold Manufacturing
- How Predictive Maintenance for Molds Boosts Performance







