Introduction
Mold production is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, impacting industries from automotive to consumer goods. This mold manufacturing guide provides an in-depth look at the entire process—from design and material selection to production techniques and quality control. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced professional, this guide will help you understand how to optimize your molds for efficiency, durability, and precision, while keeping up with the latest technological advancements.
Understanding the Basics of Mold Manufacturing
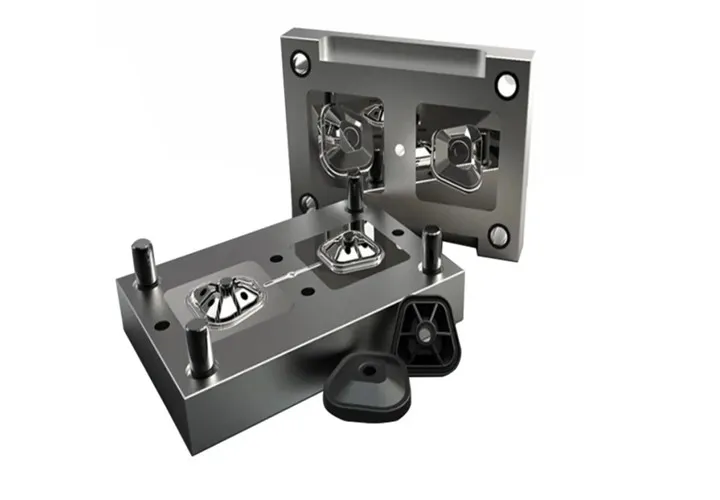

What is Mold Manufacturing?
Mold manufacturing is the process of designing and producing molds—hollow forms used to shape materials such as metals, plastics, or resins into precise products. In this mold manufacturing guide, we explore how molds are essential for industries that require high-volume production, ensuring consistent quality, accuracy, and efficiency across every component.
Types of Molds:
- Injection Molds: These molds are used to inject molten material into a cavity, allowing the production of complex, high-volume parts with precise dimensions.
- Compression Molds: Commonly used for rubber or plastic components, where the material is placed into the mold cavity and compressed to form the desired shape.
- Blow Molds: Ideal for manufacturing hollow objects such as bottles or containers by inflating molten material within the mold.
- Die Molds: Frequently used in metalworking processes like casting and forging to create durable and precise metal parts.
This section of our mold manufacturing guide highlights the key mold types and their applications, providing a foundation for understanding modern mold production techniques
Mold Design and Planning
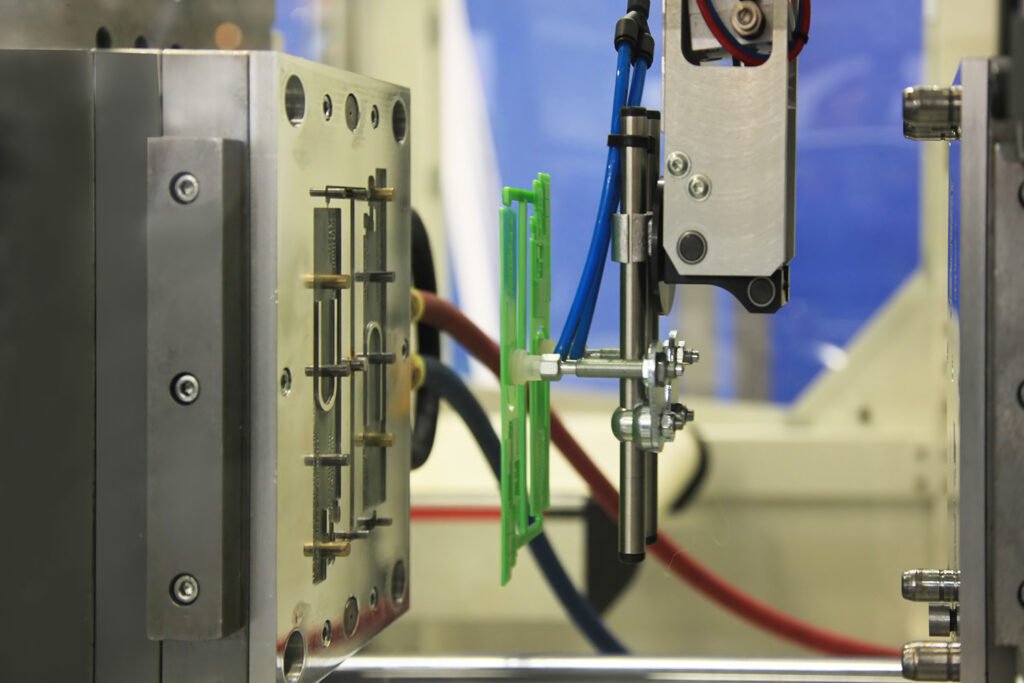
Designing the Mold:
The first step in mold manufacturing is designing the mold itself. A well-executed mold design requires a deep understanding of the material being used, the intended function of the part, and the level of precision required. Most modern mold designs are created using Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software, which enables engineers to produce detailed, accurate 3D models. This step is critical in any mold manufacturing guide, as it ensures that the final mold will produce parts that meet quality, consistency, and performance standards.
Key Design Considerations:
When following a mold manufacturing guide, several critical factors must be addressed to ensure the mold produces high-quality parts:
- Part Geometry: The mold must accurately create the intended part shape, taking into account parting lines, draft angles, and undercuts. Proper attention to geometry ensures consistent part quality and easy demolding.
- Material Selection: Choosing the right mold material is essential, as it affects both the design and production process. Common materials include steel, aluminum, and specialized alloys, each offering different strengths, durability, and thermal properties.
- Mold Cooling: Efficient cooling channels are a key element in reducing cycle times and preventing defects. Properly designed cooling systems enhance productivity and maintain the integrity of the final product.
- Mold Durability: A durable mold ensures long-term performance, allowing repeated use without excessive wear or deformation. Durability considerations are vital in any comprehensive mold manufacturing guide to guarantee consistent quality across large production runs.
Mold Simulation:
According to a complete mold manufacturing guide, simulations play a crucial role before physical production begins. By using advanced mold simulation tools, manufacturers can predict potential issues such as material flow, temperature distribution, and cooling rates. These insights allow engineers to refine the mold design, optimize the production process, and reduce the risk of defects, ensuring higher efficiency and consistent part quality.
Material Selection for Mold Making
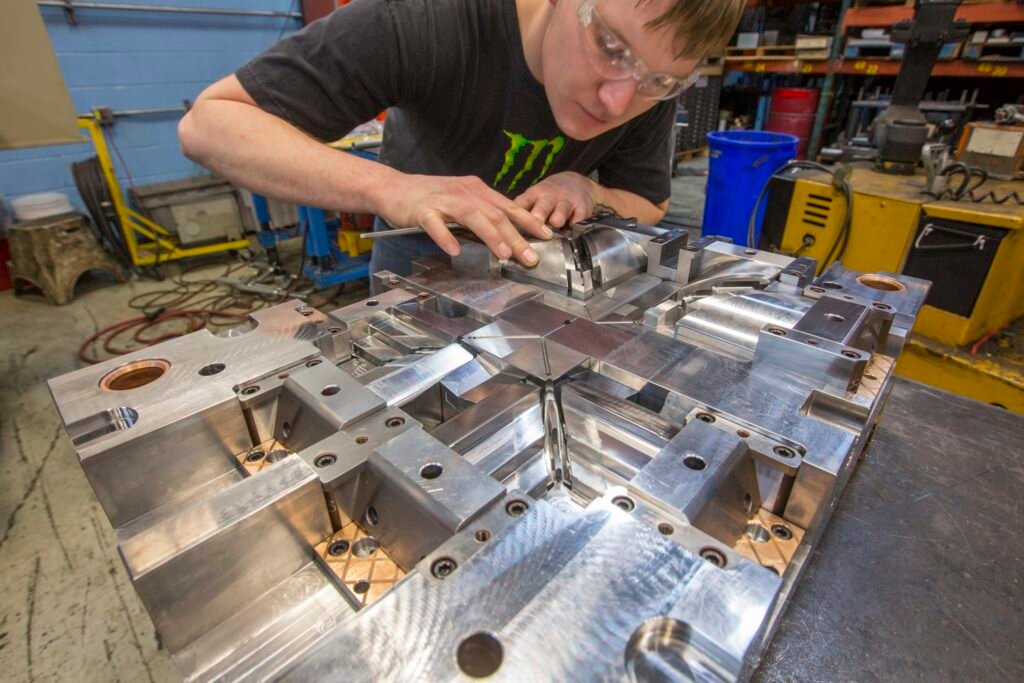
Choosing the Right Mold Material
A key step in any comprehensive mold manufacturing guide is selecting the appropriate material for mold construction. The material directly impacts the mold’s longevity, performance, and suitability for specific applications. Common mold materials include:
- Tool Steel: Known for its high durability and wear resistance, making it ideal for high-volume injection molds.
- Aluminum: Lightweight and easy to machine, aluminum is suitable for prototypes and lower-volume production.
- Stainless Steel: Offers excellent corrosion and heat resistance, making it perfect for molds used in automotive, medical, or other high-demand industries.
The choice of material should consider factors such as production volume, compatibility with the molded material, and required precision, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency.
Mold Manufacturing Process: Step-by-Step
According to a complete mold manufacturing guide, the process involves several key stages, each essential to producing a final product that meets strict quality standards and precise specifications. Every step, from design to finishing, plays a crucial role in ensuring consistency, durability, and performance in the finished molds.
Stage 1: Mold Making
In this mold manufacturing guide, CNC machining plays a vital role by using Computer Numerical Control machines to accurately cut, mill, and shape mold materials according to the detailed design specifications.
For molds requiring intricate features or precise holes, Electrode Machining, also known as Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM), is often employed to achieve complex geometries that are difficult to produce with traditional methods.
Once all components are precisely machined, the assembly stage ensures that every part fits perfectly, forming a complete and fully functional mold ready for production.
Stage 2: Mold Testing
As part of this mold manufacturing guide, before starting full-scale production, the mold undergoes rigorous testing and validation. Test shots are produced to ensure that every part meets the required specifications and quality standards.
During this stage, potential issues such as improper material flow, inadequate cooling, or difficulties with part ejection are carefully evaluated. Any necessary adjustments are made to optimize the mold’s performance, ensuring reliable and consistent production when full-scale manufacturing begins.
Stage 3: Production and Finishing
In this mold manufacturing guide, a critical step before full-scale production is rigorous testing and validation of the mold. Test shots are produced to verify that each part meets the required specifications, quality standards, and performance criteria.
During this phase, potential issues such as material flow inconsistencies, insufficient cooling, or part ejection problems are carefully assessed. Any necessary modifications are implemented to optimize mold performance, ensuring that the mold delivers consistent, high-quality output throughout the production process.
Mold Maintenance and Care
Why Maintenance Matters:
In this mold manufacturing guide, proper maintenance is essential to maximize mold lifespan and ensure consistent, high-quality production. Molds are significant investments, and neglecting regular upkeep can result in defects, reduced precision, and costly downtime. Implementing a proactive maintenance schedule helps manufacturers maintain optimal mold performance, prevent unexpected failures, and protect their investment in the long term.
Key Maintenance Tasks:
As highlighted in this mold manufacturing guide, regular cleaning of molds is crucial to remove debris and material residues that can affect part quality and mold performance.
Lubrication of all moving components reduces friction and wear, ensuring smooth operation throughout production cycles.
Inspection is another key aspect, involving careful checks of cavity surfaces, cooling channels, and other critical mold components. Routine inspections help identify potential damage or early wear, preventing costly downtime and ensuring consistent, high-quality production.
Mold Repair:
As part of this mold manufacturing guide, it’s important to recognize that molds occasionally require repairs, such as replacing worn-out components or addressing cracks. Performing timely repairs is often more cost-effective than fully replacing the mold, particularly for high-volume production molds. Proper maintenance and repair not only extend the mold’s lifespan but also ensure consistent product quality and reduce unplanned production downtime.
Common Challenges in Mold Manufacturing
Even experienced mold manufacturers face challenges throughout the process. Common issues include:
- Material Flow Problems: Inconsistent material flow can lead to part defects or incomplete filling of the mold.
- Tool Wear: Over time, molds wear out due to repeated use, causing parts to lose precision.
- Cooling Issues: Inadequate cooling can result in unevenly cooled parts, leading to warping or defects.
Overcoming these challenges requires a combination of experience, technology, and quality control.
Conclusion
Mold manufacturing is a detailed and precise process that spans multiple stages, from design and material selection to testing, maintenance, and repairs. By following each step outlined in this mold manufacturing guide, you can ensure that the molds you produce meet the highest standards of quality, durability, and performance.
Whether you are a beginner or an experienced professional, mastering the processes described in this mold manufacturing guide will enable you to create molds capable of delivering consistent, high-quality parts that stand the test of time and support efficient, reliable production.
FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. What are the different types of molds used in manufacturing?
The main types of molds include injection molds, compression molds, blow molds, and die molds, each used for different production processes and materials.
2. Why is mold design so important?
Mold design is crucial because it affects the part’s functionality, appearance, and overall production efficiency. A well-designed mold ensures quality parts with minimal defects.
3. How can mold manufacturers ensure the longevity of their molds?
By regularly maintaining molds, using quality materials, and adopting best practices in production, manufacturers can ensure their molds last longer and perform optimally.
4. What are the most common issues in mold manufacturing?
Common issues include material flow problems, tool wear, cooling inefficiencies, and design flaws. Addressing these challenges early on can prevent defects and delays.
5. How does mold testing work?
Mold testing involves running initial production cycles to identify issues such as material flow, cooling, and part ejection. This allows for adjustments before full-scale production begins.
Sources:
- Moldmaking Technology – Complete Guide to Mold Manufacturing
- Modern Machine Shop – CNC Machining for Mold Making
- The Engineer – Essential Guide to Mold Manufacturing







