Introduction
The medical device manufacturing industry is one of the most stringent and innovation-driven sectors, where precision, reliability, and quality are paramount. Molds play a central role in this process, enabling the production of high-quality components that meet rigorous regulatory standards. From surgical tools to diagnostic equipment and implants, molds are indispensable in shaping the future of medical device manufacturing. This article explores the critical role of molds in the creation of medical devices, emphasizing how they drive innovation and ensure safety and performance in healthcare applications.
1. Precision and Quality in Medical Devices
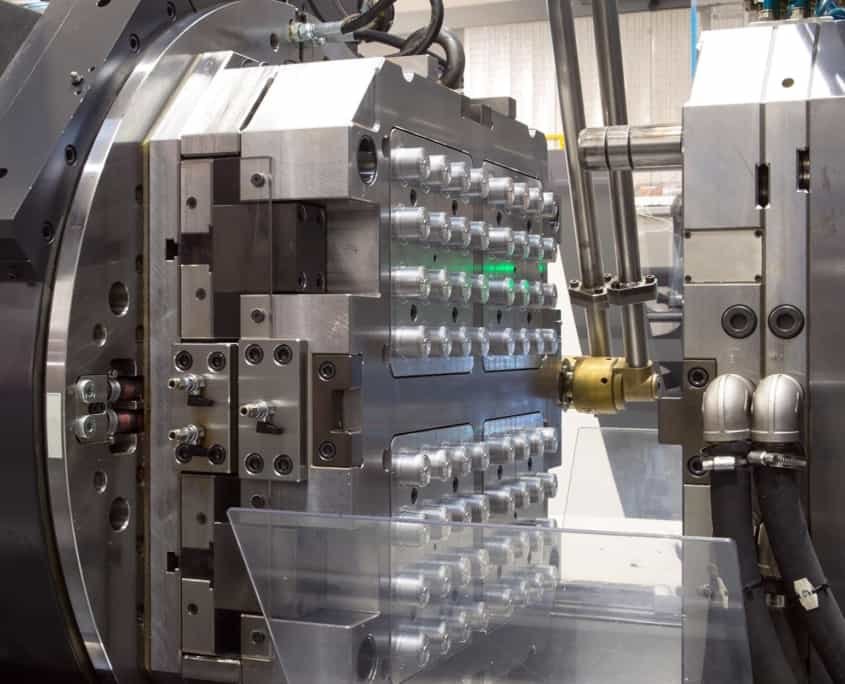
Role of Molds:
Molds are crucial for ensuring the precision and consistency of medical devices. Whether producing components for implants, syringes, diagnostic instruments, or surgical tools, molds ensure that each part is manufactured to exact specifications. The use of advanced molding techniques such as injection molding, blow molding, and compression molding guarantees that each part is produced with the required dimensional accuracy.
How Molds Drive Innovation:
In medical device manufacturing, even the smallest error in the production process can have significant consequences. Molds allow for high-precision production, which is essential for the performance and safety of medical devices. The ability to design intricate, detailed components that meet strict quality standards ensures that medical devices function as intended and improve patient outcomes.
2. Material Versatility for Complex Designs
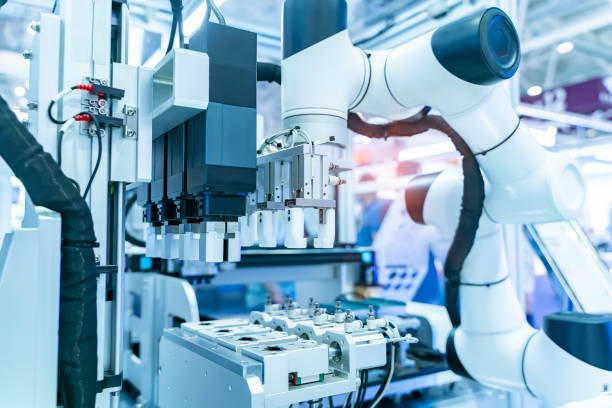

Role of Molds:
Medical devices often require a combination of different materials to achieve desired properties, such as biocompatibility, flexibility, and durability. Molds are used to produce components in a wide variety of materials, including metals, plastics, ceramics, and composites. Advanced molding techniques allow for the use of materials with specific properties needed for medical applications, such as medical-grade plastics for disposable devices or metals for implants.
How Molds Enable Complex Designs:
Molds facilitate the use of complex designs in medical devices, such as those with fine details or multi-component structures. For instance, injection molding allows for the creation of devices with intricate shapes and internal cavities, which would be difficult or impossible to produce using traditional manufacturing methods. This flexibility in material choice and design capability enables manufacturers to innovate and create devices that are tailored to specific medical needs.
3. Cost-Effectiveness in Production
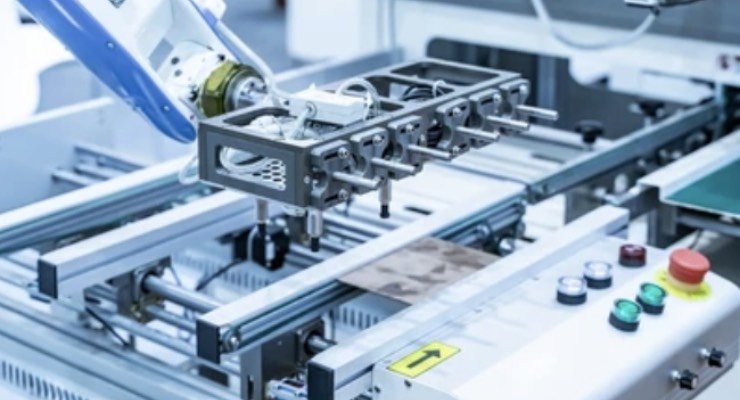

Role of Molds:
In medical device manufacturing, cost-efficiency is a key consideration. Molds allow for high-volume production of medical device components, reducing the cost per unit and making it more affordable to meet global demand. By enabling the rapid production of identical parts, molds can significantly decrease labor costs, minimize material waste, and streamline the production process.
How Molds Drive Cost-Effective Innovation:
Molds not only provide precision but also ensure that manufacturers can produce devices at scale, which is crucial for driving down costs. Additionally, advanced mold technologies, such as automated molding systems, further enhance production speed and accuracy, enabling manufacturers to meet tight deadlines and regulatory requirements without compromising on quality. This cost-effective approach allows for continuous innovation while keeping prices affordable for healthcare providers and patients.
4. Regulatory Compliance and Safety Standards
Role of Molds:
The medical device industry is heavily regulated, with strict standards governing the production of devices to ensure patient safety. Molds must meet high-quality standards and be able to produce parts that comply with various regulatory requirements, including ISO certifications and the FDA’s Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP).
How Molds Ensure Compliance:
Molds are designed and manufactured with the utmost attention to detail to meet regulatory compliance. Advanced molding techniques ensure that the components produced are free of defects and meet the required tolerances. Additionally, the materials used in the molding process must be biocompatible and safe for use in medical applications. The precision and repeatability of molded parts are essential for maintaining compliance and meeting safety standards.
5. Customization for Patient-Specific Devices
Role of Molds:
One of the significant advantages of molding in medical device manufacturing is its ability to produce customized devices for specific patient needs. From orthopedic implants to dental prosthetics and hearing aids, molds can be used to create patient-specific devices that are tailored to fit the individual’s anatomy.
How Molds Enable Customization:
Custom molding techniques allow manufacturers to create devices that match the precise specifications of a patient’s body, improving the fit and functionality of medical devices. This customization leads to better outcomes for patients, as personalized devices offer improved comfort and effectiveness compared to mass-produced alternatives. The ability to mold complex shapes with high precision is particularly beneficial in fields such as prosthetics and orthotics.
6. Enhancing Sterility and Cleanliness
Role of Molds:
In the medical device industry, cleanliness and sterility are crucial. Many devices, especially those used in surgical procedures or for direct contact with the human body, need to be free from contaminants. Molds help ensure that medical components are produced in clean environments and can be easily sterilized before use.
How Molds Contribute to Sterility:
Molds used in the production of medical devices are often designed to minimize the risk of contamination during the manufacturing process. Additionally, molded parts can be easily cleaned and sterilized, which is essential for preventing infections and ensuring patient safety. The ability to create smooth, non-porous surfaces through molding helps to reduce the risk of bacterial growth on medical devices.
7. Supporting Innovation in Wearable Medical Technology
Role of Molds:
The growing demand for wearable medical devices—such as monitoring systems, sensors, and fitness trackers—has spurred innovation in mold technology. These devices need to be lightweight, comfortable, and capable of withstanding daily wear and tear.
How Molds Enable Wearable Tech Innovation:
Molds are used to produce components that are both lightweight and durable, crucial for wearable medical devices. The ability to mold flexible, biocompatible materials into compact, ergonomic shapes ensures that wearable devices are comfortable for extended use. This innovation in mold technology allows manufacturers to create medical devices that continuously monitor health metrics, providing real-time data to both patients and healthcare providers.
Conclusion
Molds are at the heart of medical device manufacturing, playing an essential role in producing high-quality components that meet stringent regulatory standards. From precision and material versatility to cost-effectiveness and customization, molding technology drives innovation across a wide range of medical applications. As the healthcare industry continues to evolve, the importance of molds in creating safe, reliable, and innovative medical devices will only grow, enabling the development of new technologies that improve patient care and outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: How do molds contribute to the safety of medical devices?
A: Molds ensure that medical device components are produced with high precision and quality, reducing the risk of defects. This ensures that devices meet safety standards and function reliably during use, which is critical in medical applications.
Q2: What materials are commonly used in medical device molding?
A: Common materials include biocompatible plastics (such as medical-grade polyethylene and polycarbonate), metals (for implants and surgical tools), and silicone (for flexible components). The material is chosen based on the device’s application and required properties.
Q3: Can molds be used to create custom medical devices?
A: Yes, molds are ideal for creating custom medical devices tailored to a patient’s specific needs, such as implants, prosthetics, and hearing aids, improving comfort and functionality.
Q4: How does molding ensure compliance with medical device regulations?
A: Molding allows manufacturers to produce parts that meet exact regulatory standards, including ISO certifications and FDA regulations. The precision of molded components helps ensure that medical devices function as intended, meeting all safety and performance criteria.
Q5: What is the role of molds in the production of wearable medical technology?
A: Molds are used to create lightweight, durable, and comfortable components for wearable medical devices, ensuring they are both functional and ergonomic for continuous use by patients.
Sources:
Medical Device Manufacturing – “The Role of Molds in Healthcare Innovations.”
Healthcare Technology – “How Molding Shapes the Future of Medical Devices.”
Plastics Engineering – “Advances in Molding Techniques for Medical Applications.”
Suggested Topics







